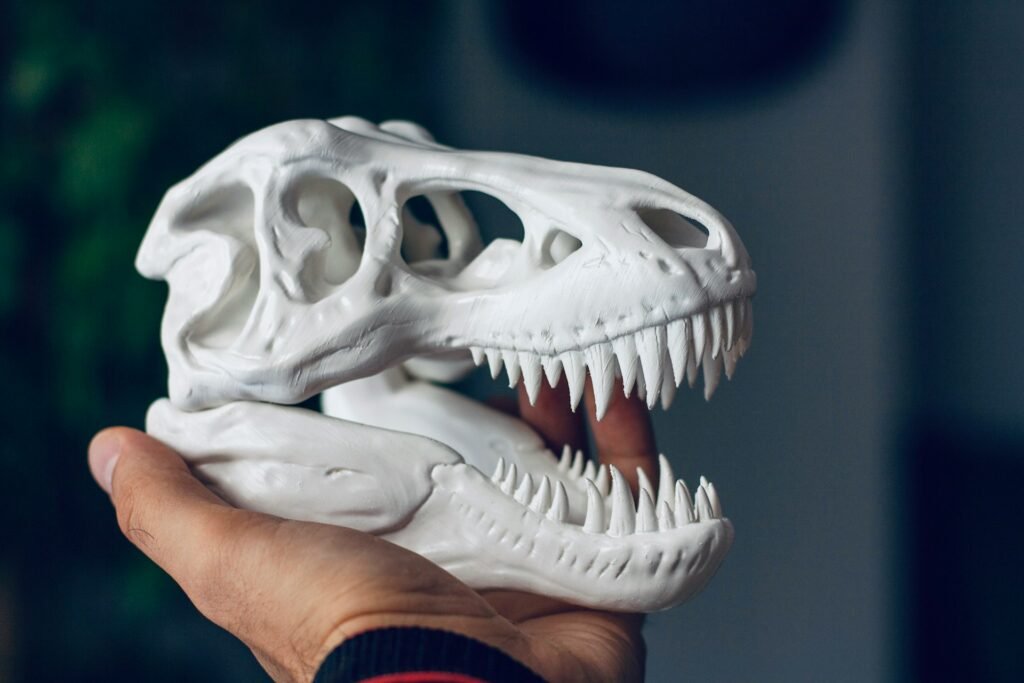
A Beginner’s Guide to 3D Printing Filaments and Their Properties
3D printing has revolutionized the way we create and innovate, but to get the best results from your 3D printer, understanding the different types of filaments and their properties is crucial. Here, we’ll explore the most common types of 3D printing filaments and their unique characteristics.
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
Properties:
- Biodegradable: Made from renewable resources like corn starch and sugarcane.
- Easy to Print: PLA has a low printing temperature and minimal warping, making it beginner-friendly.
- Smooth Finish: Produces a glossy finish, ideal for aesthetic models and prototypes.
Uses:
- Prototypes
- Decorative items
- Educational projects
Pros:
- Environmentally friendly
- Low odor during printing
- Wide color availability
Cons:
- Lower strength and durability compared to other filaments
- Not suitable for high-temperature applications
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Properties:
- Durable and Strong: Known for its impact resistance and toughness.
- Higher Printing Temperature: Requires a heated bed to prevent warping.
- Smooth Finish: Can be post-processed with acetone vapor for a glossy finish.
Uses:
- Functional prototypes
- Automotive parts
- Toys
Pros:
- High durability
- Good heat resistance
- Can be sanded and painted easily
Cons:
- Produces fumes; requires good ventilation
- Warping can be an issue without a heated bed
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-Modified)
Properties:
- Strong and Flexible: Combines the ease of printing of PLA with the strength and durability of ABS.
- Chemical Resistant: Resistant to water and chemicals.
- Clear and Glossy Finish: Can be printed with a transparent or glossy look.
Uses:
- Food containers
- Mechanical parts
- Water bottles
Pros:
- Easy to print
- Durable and flexible
- Food safe (ensure food-grade certification)
Cons:
- Can be stringy during printing
- Requires fine-tuning of print settings
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
Properties:
- Flexible and Elastic: Known for its rubber-like properties.
- Abrasion Resistant: High resistance to wear and tear.
- Shock Absorbent: Good for impact-resistant applications.
Uses:
- Phone cases
- Wearable items
- Flexible joints
Pros:
- High flexibility
- Durable and impact-resistant
- Good for vibration dampening
Cons:
- More difficult to print than PLA or ABS
- Requires slow printing speeds
Nylon
Properties:
- High Strength and Durability: Excellent for mechanical parts and functional prototypes.
- Flexible: Can withstand significant stress without breaking.
- Abrasion Resistant: Ideal for parts that experience friction.
Uses:
- Gears and bearings
- Structural components
- Tools
Pros:
- Strong and durable
- Flexible and impact-resistant
- Good for functional parts
Cons:
- Requires high printing temperature
- Absorbs moisture, needs to be stored properly
PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol)
Properties:
- Water-Soluble: Dissolves in water, making it ideal for support structures.
- Biodegradable: Environmentally friendly.
- Easy to Remove: Supports can be easily removed by submerging the print in water.
Uses:
- Support material for complex prints
- Dissolvable supports in dual-extrusion printers
Pros:
- Easy removal of supports
- Ideal for complex geometries
- Biodegradable
Cons:
- Sensitive to moisture, requires proper storage
- Can be expensive
Choosing the right 3D printing filament depends on your project requirements. PLA is great for beginners and decorative items, ABS is suitable for durable parts, PETG offers a balance between strength and ease of use, TPU is perfect for flexible objects, Nylon is excellent for mechanical components, and PVA is ideal for support structures.
Understanding the properties of each 3D printing filaments type will help you make informed decisions, ensuring the success of your 3D printing projects. Happy printing!